
Storage-based data deduplication reduces the amount of storage needed for a given set of files. Examples are CSS classes and named references in MediaWiki. In computer code, deduplication is done by, for example, storing information in variables so that they don't have to be written out individually but can be changed all at once at a central referenced location. Deduplication is often paired with data compression for additional storage saving: Deduplication is first used to eliminate large chunks of repetitive data, and compression is then used to efficiently encode each of the stored chunks. With data deduplication, only one instance of the attachment is actually stored the subsequent instances are referenced back to the saved copy for deduplication ratio of roughly 100 to 1. Each time the email platform is backed up, all 100 instances of the attachment are saved, requiring 100 MB storage space.
These chunks are identified and stored during a process of analysis, and compared to other chunks within existing data.
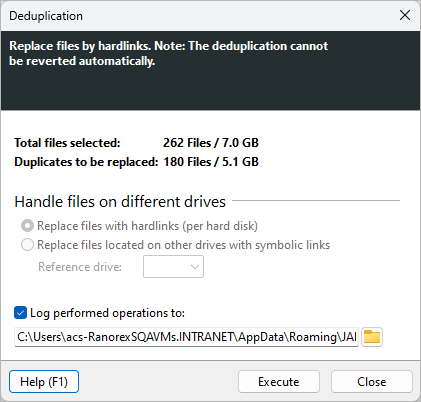
The deduplication process requires comparison of data 'chunks' (also known as 'byte patterns') which are unique, contiguous blocks of data. It can also be applied to network data transfers to reduce the number of bytes that must be sent.

Successful implementation of the technique can improve storage utilization, which may in turn lower capital expenditure by reducing the overall amount of storage media required to meet storage capacity needs.

In computing, data deduplication is a technique for eliminating duplicate copies of repeating data. Data processing technique to eliminate duplicate copies of repeating data


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
